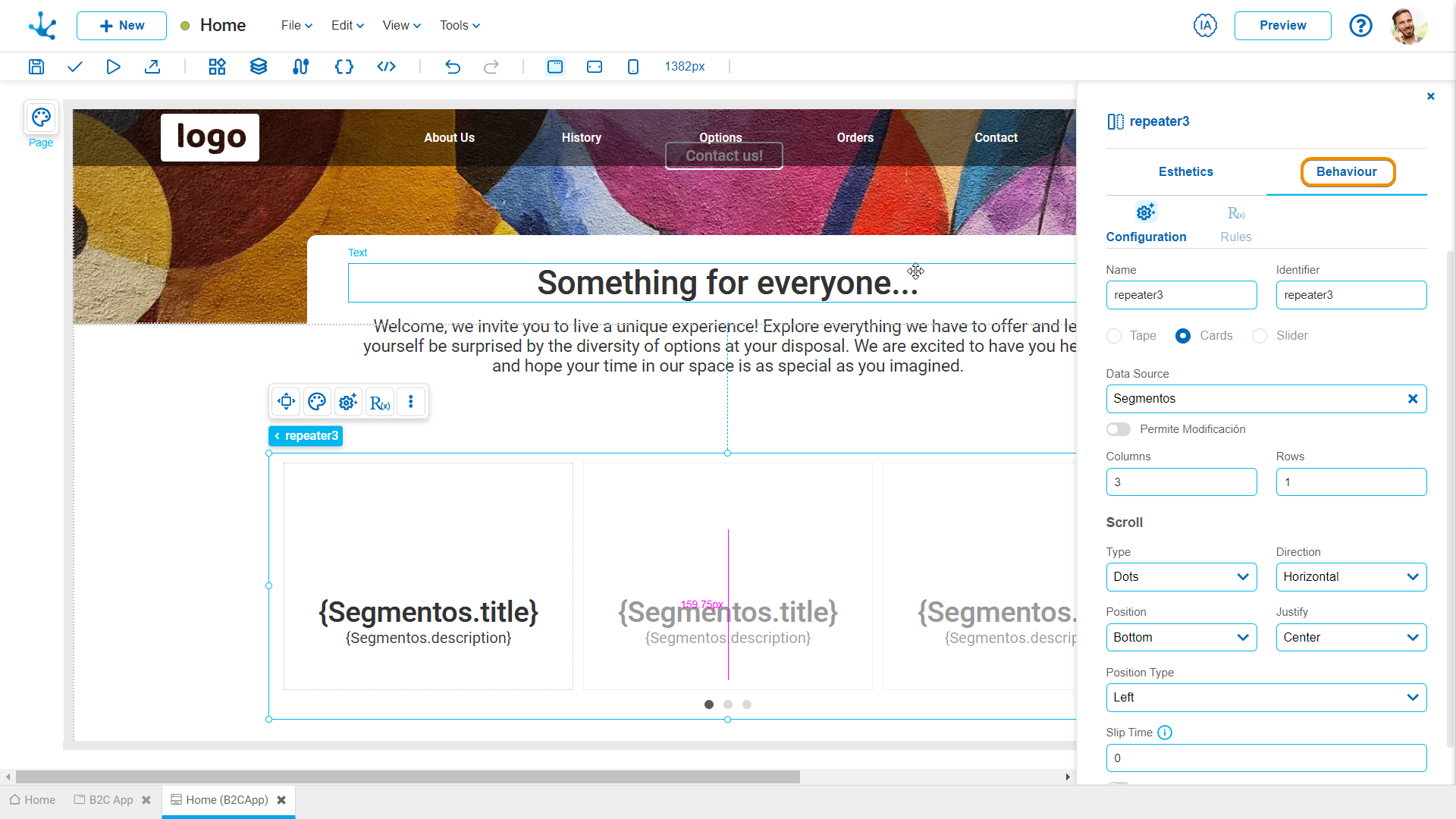
Repeater
The repeater element allows to display a set of retrieved instances by a data source, unlike other elements that only allow a single instance to be displayed.
Visually it is similar to the layout element but only the first item can be modified and a data source must be defined. Such item repeats as many times as instances are obtained from the data source.
If the items included in the repeater show information on the instances of the data source defined in it, such source must be previously configured.
The element properties are represented by icons in its context menu, where its operations are also available.
Subtypes
When selecting the option "Repeater" from the icon ![]() in the top toolbar, a list opens with the different subtypes of this element, which can be dragged and dropped into the modeling area. Each subtype has the element's properties modeled and built in a specific way.
in the top toolbar, a list opens with the different subtypes of this element, which can be dragged and dropped into the modeling area. Each subtype has the element's properties modeled and built in a specific way.
•Cards
•Tape
•Slider
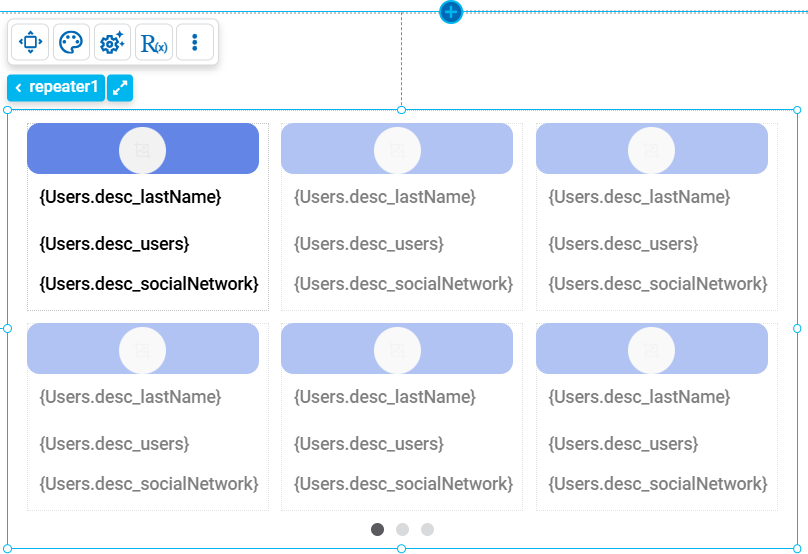
Cards
This type of repeater organizes its content in a visual card format, where each card acts as an independent unit that may contain different elements with values obtained from a data source. This type of repeater is ideal for representing structured content in an attractive and functional way.
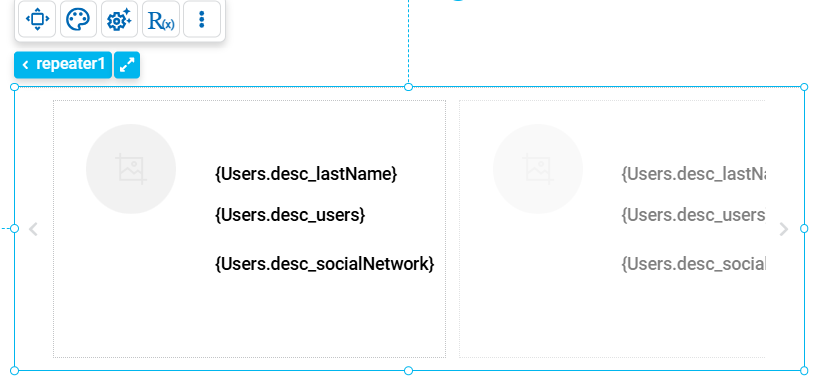
Tape
This type of repeater organizes elements in a horizontally movable structure, as if they were part of a continuous tape. It is ideal for displaying content that may come from a data source, in a limited space, while allowing users to explore more elements using browsing controls.
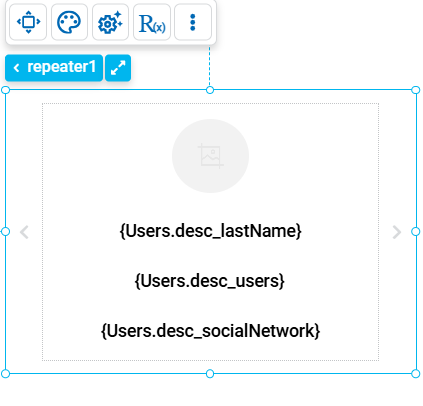
Slider
This type of repeater organizes elements in an interactive format that can be scrolled horizontally or vertically. It is ideal for displaying featured content, such as images, products or news, in an interactive and compact way, with values obtained from a data source.
Classification of Properties
Properties are divided into two groups: esthetic properties and behavior properties.
Esthetic Properties
In the esthetic properties panel, the following are grouped:
Behavior Properties
In the behavior properties panel, the following are grouped: