Low Code Development for Claims Management
November 21, 2024
AI + Low Code and No Code: Smart Combination
January 14, 2025Low Code Platforms: Speed to Innovation


Agility it is a crucial factor in today's business environment, where the ability to adapt quickly to market changes can determine the success or failure of a company.

Agility is a crucial factor in today's business environment, where the ability to quickly adapt to market changes can determine a company's success or failure.

According to a report by Forrester, 84% of companies are migrating to the use of Low Code platforms to reduce the pressure on their IT resources. This could become a critical element for in-house software development, a solution increasingly implemented by high-performance organizations seeking to foster innovation and competitiveness in the market.
What is Low Code?
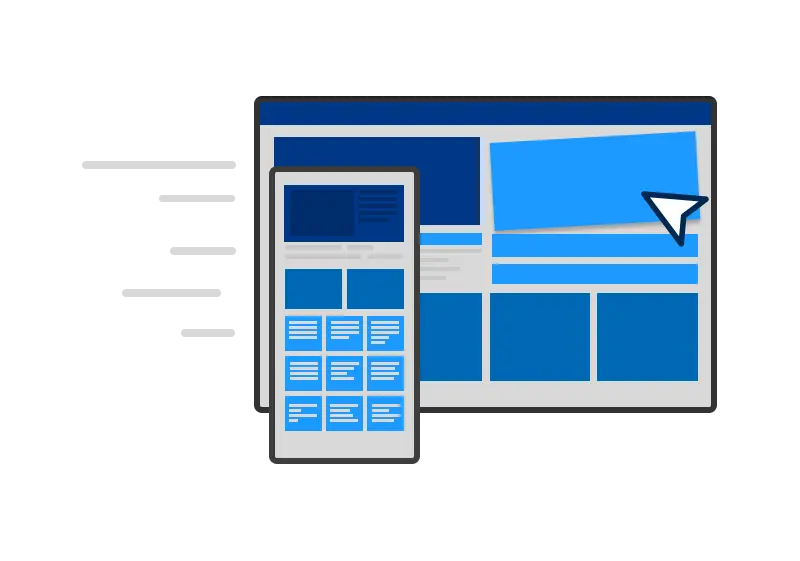
Low code is a visual software development approach that simplifies application creation by minimizing the need for traditional, complex hand coding. It features an easy-to-use, drag-and-drop development environment that makes application development accessible to both novice and experienced programmers. This approach enables faster, more inclusive, and streamlined enterprise software creation and innovation. Low code development platforms are increasingly popular in the business world for their efficiency and ease of use.
These innovative digital solutions have proven effective in improving business processes across a variety of industries. Manufacturing companies, insurance organizations, financial firms, and more streamline their operations and respond quickly to market changes using low-code platforms.
Characteristics of Low Code Platforms
Low-code platforms offer a number of features that significantly differentiate them from traditional software development methods. Key features of low-code platforms are summarized below:
Comparison between traditional software development and Low Code
Comparing low-code platforms to traditional software development methods highlights several important differences:
| Speed of development | Costs | Accessibility | Flexibility and customization | Maintenance and update | Scalability | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low Code | Significant acceleration in application development thanks to visual tools and pre-built components. | Reduced costs in terms of time and human resources; reduced need for highly specialized developers. | Accessible to business users and citizen developers, no deep programming knowledge required. | It offers enough flexibility and customization for most enterprise applications, but may have limitations for very specific or complex projects. | It facilitates maintenance and updates thanks to its intuitive interfaces and reusable components. | Suitable for applications that can scale with business growth, although there may be limitations on extremely large and complex applications. |
| Traditional | It requires manual coding from scratch, which can be slow and laborious. | Greater investment in specialized developers and longer development time. | It requires advanced programming skills, limiting application creation to professional developers. | Maximum flexibility and customization, suitable for highly specialized and complex projects. | Maintenance and upgrades can be more complex and expensive due to the need to manually modify and test code. | Scalable according to the needs of the project, without the limitations that some low-code platforms may impose. |
Speed of development
Low Code
Significant acceleration in application development thanks to visual tools and pre-built components.
Traditional Development
It requires manual coding from scratch, which can be slow and laborious.
Costos
Low Code
Reduced costs in terms of time and human resources; reduced need for highly specialized developers.
Traditional Development
Greater investment in specialized developers and longer development time.
Accesibilidad
Low Code
Accessible to business users and citizen developers, no deep programming knowledge required.
Traditional Development
It requires advanced programming skills, limiting application creation to professional developers.
Flexibility and customization
Low Code
It offers enough flexibility and customization for most enterprise applications, but may have limitations for very specific or complex projects.
Traditional Development
Maximum flexibility and customization, suitable for highly specialized and complex projects.
Maintenance and update
Low Code
It facilitates maintenance and updates thanks to its intuitive interfaces and reusable components.
Traditional Development
Maintenance and upgrades can be more complex and expensive due to the need to manually modify and test code.
Scalability
Low Code
Suitable for applications that can scale with business growth, although there may be limitations on extremely large and complex applications.
Traditional Development
Scalable according to the needs of the project, without the limitations that some low-code platforms may impose.
Main advantages of Low Code platforms

Increasing corporate agility
By reducing development time, companies can adapt more quickly to market changes and customer needs.

Empowering business users
A low-code platform like Deyel enables users with limited technical knowledge to develop applications, reducing dependency on the IT department.

Cost reduction
Speed of development and deployment reduces costs associated with traditional software development.
Corporate use cases with Low Code
Low Code begins in the world
The origin of Low Code dates back to the early 2000s, when the first tools designed to facilitate the development of applications without the need to write large amounts of code emerged. These tools were born out of the need to reduce the complexity and time required to develop software, allowing users with little or no programming experience to create functional applications.
One of the pioneers in this field was the company OutSystems, founded in 2001 by Paulo Rosado in Portugal. Over time, the demand for more agile solutions and the need for digitalization in companies, drove the growth of the Low Code platform market. In the mid-2010s, the concept gained greater traction and visibility, consolidating itself as a key trend in the software industry.

Beginnings of Low Code in Latin America
In Latin America, the adoption of low-code platforms began to gain traction in the mid-2010s, in parallel with the global trend. However, several region-specific factors have influenced the way these technologies have been adopted and adapted.
Emerging economies in Latin America have experienced a strong push towards digitalization. Companies of all sizes have sought solutions that allow them to modernize their processes and offer digital services more efficiently. Low Code has been seen as an essential tool to achieve these objectives without the need for a large investment in traditional development resources.
The region has faced a significant shortage of skilled software developers. This has made low-code platforms especially attractive, as they enable people with limited technical skills to develop complex applications. This has democratized software development and allowed more people to contribute to digital innovation within their organizations.
Several companies in the region have been pioneers in the adoption of Low Code. For example, companies such as TOTVS in Brazil have integrated Low Code technologies into their solutions to offer more agile and adaptable products. In addition, the region has seen the emergence of local Low Code platform providers and startups that are developing solutions tailored to the specific needs of the Latin American market.
Some governments in the region have recognized the importance of digital transformation and have launched initiatives to encourage the adoption of advanced technologies, including Low Code platforms. These initiatives have helped accelerate adoption in sectors such as education, health and public services..
Although low code adoption in Latin America started a bit later than in other regions, it has grown rapidly due to the demand for digitalization, the shortage of developers, and the support of companies and governments. Today, low code platforms are playing a crucial role in the digital transformation of the region.
Low Code + IA
The combination of low-code platforms with artificial intelligence (AI) is changing the way companies develop applications and optimize their processes. Low-code platforms allow users without programming experience to create software solutions quickly and easily, while AI powers those applications with advanced capabilities such as automation, predictive analytics, and smart decision making.
Thanks to this integration, organizations can streamline application creation, automate complex tasks, and personalize experiences for their customers, without relying exclusively on IT departments. The synergy between Low Code and AI accelerates innovation and makes organizations more competitive in the market.
Opiniones de expertos
en Low Code + IA
A recent study by consulting firm Gartner predicts that by 2025, 70% of new applications developed by organizations will use low-code or no-code technologies, up from less than 25% in 2020. According to the report, the rise of low-code application platforms “is driving the rise of citizen development, and in particular, the role of business technologists who report outside of IT departments and build technology or analytics capabilities for internal or external business use.”
In 2021, the global low-code development platform market was valued at $7.61 billion. It is expected to surpass $36 billion by 2027, registering a compound annual growth rate of nearly 30% between 2022 and 2027.
These studies and opinions provide a detailed insight into how business specialists perceive the impact of Low Code platforms on companies.